

|
MODERN CONTROL FOR ENERGY SYSTEMS
a.y. 2017-2018 Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria Energetica |
 |
| Instructor |
Prof. Luca Schenato
Phone: 049 827 7925
Office: 315 DEI/A
E-mail: ![]() ( NO
luca.schenato@dei.unipd.it !!!!)
( NO
luca.schenato@dei.unipd.it !!!!)
Webpage: http://automatica.dei.unipd.it/people/schenato.html
Office hours: appointment by
email or phone
| Description |
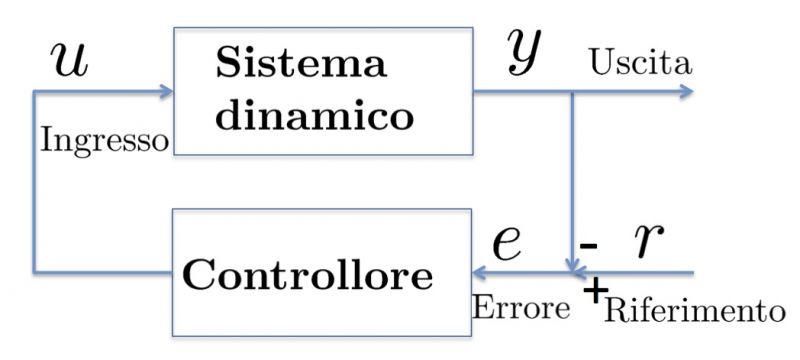
- Mathematical modeling of dynamical systems
- Definitions and mathematical model classes for dynamical systems
- Representation in State Space
- Linear Systems
- Stability and Lyapunov theory
- Linearization around working points
- Transient and stationary responce to step, impulse and sinuisoidal inputs
- Relevant LTI systems: I and II order systems
- Laplace transform
- Frequency domain control: PID controllers
| Lectures |
Each lecture references the specific textbook sections
| Week |
MONDAY (10:30-12:30 classroom M4) |
THURSDAY (12:30-14:15 classroom M3) |
|
|
1 (25-28/09) |
Class Introduction (Slides)
Water Tank, Car on inclined plane |
DC Motor, Heat-Trasfer, Building temperature dynamics, Hydraulic piston, Temperature regulator | |
|
2 (2-5/10) |
Water level regulator, electronic circuit (Astrom-Murray, exercise 3.4). Recup in Linear Algebra: determinant, rank, image, kernel,etc.. |
Jordan form. Exponential of a matrix. Solution of LTI systems.(Chaper 5 of Astrom-Murray) |
|
|
3 (9-12/10) |
Modes of LTI systems, free evolution of the output, stability (Wednesday 10/10 Room Fe) |
Equilibrium confuguration for stable LTI systems. Examples. |
|
|
4 (16-19/10) |
More example on LTI systems. |
The value of control. Nominal control and integral control. Pole placement: examples and naive approach. |
|
|
5 (23-26/10) |
Reachability definition and matrix. Reachable canonical form. Pole placement problem. Ackerman formula. |
Example of desing of state-feedback control |
|
|
6 (30/10-2/11) |
INTRODUCTION TO SIMULINK (Room Te) |
MATLAB/SIMULINK: the water-tank model (Room Te) |
|
|
7 (6-9/11) |
Stability of linearized systems via Lyapunov Theory. Observability and observers |
Stability of Observers and examples. Robustness to parameter uncertainty |
|
|
8 (13-16/11) |
MATLAB/SIMULINK: nominal and robust control of the water-tank model (Room Te) |
Laplace Transform, Transfer Fucntions, Mapping from state-space to transfer function and vice-versa. Definition zeros and poles, Bode Diagrams |
|
|
9 (20-23/11) |
Example of LTI representations, Steady-state behaviour to impulse, step and sinusoidal input |
NO LECTURE |
|
|
10 (27-30/11) |
Bode Dyagrams; |
(Wednesday 29/11 8:45-10:30 Room Fe) Nyquist plots |
|
|
11 (4-7/12) |
Nyquist criterion for stability |
Stability margins. | |
|
12 (11-14/12) |
Frequency domain design of PIDs | PID desing |
|
|
13 (18-21/12) |
24 | ||
| 14 (15-18/01) | |
| Materiale |
Official textbook:
- K.J. Astrom, R.M. Murray, Feedback Systems: An introduction for Scientists and Engineers, Princeton University Press, 2008
Optional textbook:
- G.F. Franklin, J.D. Powell, Emami-Naeini, Feedback Control of Dynamical Systems, Pearson, Prentice Hall, Fifth Edition, 2006
| Control Problems |
- TBD

